Spectral Whitening (sometimes called balencing or broadening) is a process usually applied post-migration to improve the resolution and appearance of seismic data and is a crude attempt to correct for frequency attenuation. A variety of methods may be used to attempt to equalise the spectrum without overly boosting noise.
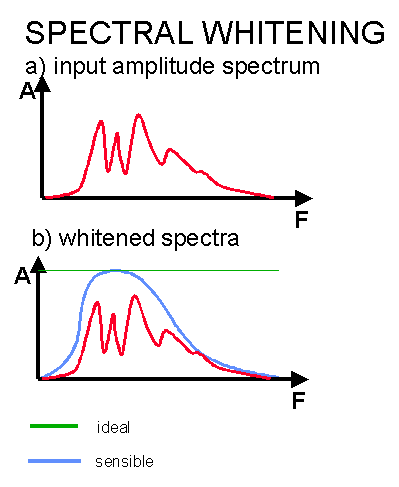
The theory of spectral whitening is described by the adjacent figure showing an input amplitude spectrum (a) of (typically) a migrated section. The objective of spectral whitening is to boost the balance of frequencies ultimately to obtain perfect resolution as shown by the green line in (b). While this spectrum could in theory be obtained, in practise it would likely result in the boosting of noise at low and high frequencies. More sensible would be to whiten the data within its own bandwidth as shown schematically by the blue curve.